What Is Below Mantle . Reddish brown spots are garnets. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle.
from www.transtutors.com
Reddish brown spots are garnets. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core.
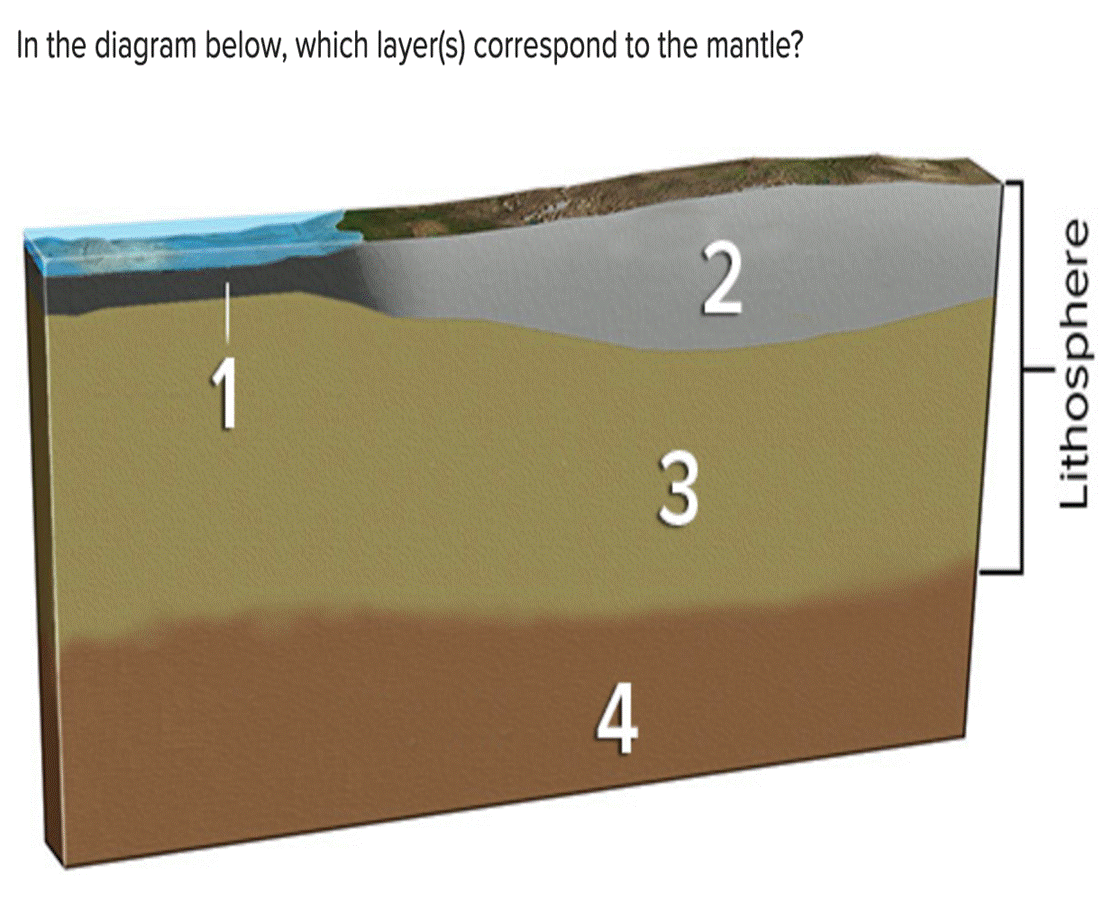
(Get Answer) n The Diagram Below, Which Layer(S) Correspond To The
What Is Below Mantle Reddish brown spots are garnets. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. Reddish brown spots are garnets. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle.
From www.thoughtco.com
6 Fascinating Facts About the Earth's Mantle What Is Below Mantle lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. It is the. What Is Below Mantle.
From smartclass4kids.com
4 Layers Of The Earth What Lies Beneath Earth's Crust What Is Below Mantle below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Reddish brown spots are garnets. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. The mesosphere is a region of strong,. What Is Below Mantle.
From dxooctqqd.blob.core.windows.net
Science Definition Lower Mantle at Barnes blog What Is Below Mantle Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. Reddish brown spots are garnets. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.teacherspayteachers.com
Composition of Earth Crust, Mantle and Core TpT What Is Below Mantle below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. . What Is Below Mantle.
From www.youtube.com
Interior of Earth Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Lower Mantle, Core What Is Below Mantle lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. Reddish brown spots are garnets. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate. What Is Below Mantle.
From nexusnewsfeed.com
New model reveals rips in Earth's mantle layer below southern Tibet What Is Below Mantle It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. lower in the mantle, extreme. What Is Below Mantle.
From printablezonedolour.z19.web.core.windows.net
Mantle Earth Science What Is Below Mantle lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2900 km. Reddish brown spots. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 Earth Science PowerPoint Presentation, free download What Is Below Mantle the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. It is the largest chemical layer by. What Is Below Mantle.
From publish.illinois.edu
A Shift to Plate Tectonics The Emergence and Evolution of Plate What Is Below Mantle lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. as plates move apart at. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Earth Science Chapter 5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download What Is Below Mantle Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. the mantle. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.engadget.com
Scientists plan to drill into the Earth's mantle for the first time What Is Below Mantle The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Reddish brown spots are. What Is Below Mantle.
From lessonfullgalleting.z21.web.core.windows.net
Earth's Crust And Mantle Answers What Is Below Mantle The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. It is the largest chemical layer by volume, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.pinterest.com
Mantle's Layers Layers the Lithosphere is the crust and uppermost What Is Below Mantle as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. Reddish brown spots are garnets. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.pinterest.com
The Earth's mantle is the portion of the that lies between the What Is Below Mantle as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. the mantle is the mostly solid bulk of earth's interior. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. lower in the mantle, extreme. What Is Below Mantle.
From quizrecentring.z21.web.core.windows.net
How Thick Is The Earth's Mantle In Km What Is Below Mantle as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. lower in the mantle, extreme pressures transform minerals and create rocks like eclogite (figure 3.4), which contains garnets. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.discovermagazine.com
Recreating the Intense Conditions of the Earth's Mantle Solves A Long What Is Below Mantle as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. The mesosphere is a region of strong, rigid. Reddish brown spots are garnets. the mantle. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.transtutors.com
(Get Answer) n The Diagram Below, Which Layer(S) Correspond To The What Is Below Mantle the mantle sits below the crust and above the core. Ophiolites are pieces of the mantle. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and. What Is Below Mantle.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Earth Layers PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4354457 What Is Below Mantle below the asthenosphere and extending to about 2,900 km is the mesosphere or lower mantle. Most of what we know about the mantle comes from seismic wave analysis, though the information is gathered by studying ophiolites and xenoliths. as plates move apart at a divergent plate boundary, the release of pressure produces partial melting of the underlying mantle.. What Is Below Mantle.